Written by Gavin Piccione
One of the most exciting perks of having an appreciation for geology is the limitless possibility to find new geologic features, even on the most seemingly mundane trips outside. It may be an interesting pebble that catches your eye or a new outcrop that piques your interest, but one usually does not have to travel far to find thought-provoking rocks. However, within this vast collection of terrestrial curiosities, some features stand out as particularly exceptional or interesting.
On a recent trip to Panther Beach, I experienced the thrill of discovering one of these remarkable geologic marvels hiding just up the coast. In this installation of Rock Record, I cover why the rocks at Panther Beach in Santa Cruz are a world-renowned sedimentary outcrop, and I investigate how this truly unique part of the cliff was deposited here.
The Rocks at Panther Beach
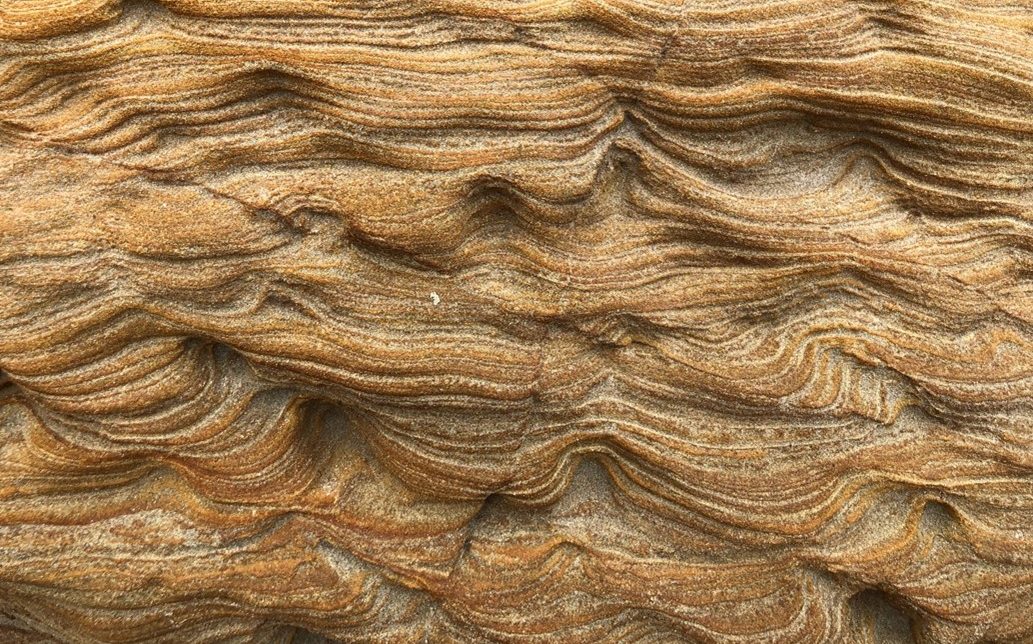
At first glance the rocks at Panther beach may look very familiar to folks who have spent time in Santa Cruz, with cliff walls of the main section of beach made up of the crumbly, beige sedimentary rock called Santa Cruz mudstone. However, if you head to the south-end of the beach, and pass under the archway, the rocks change drastically. Instead of the highly uniform mudstone, the rocks on this side are wavy, laminated sandstones (see image 1). Below these peculiar sandstones there are darker rocks, called dolomite-cemented sands, that have bands that tilt down and towards the southeast. If one breaks or scratches these dolomite-cemented sands, they may smell the faint odor of petroleum. The contact between these two rock types is high irregular, looking almost as if the dolomite-cemented sands were bubbled up into the wavy sandstones like liquid in a lava lamp (see images 2 and 3). Capping these two sandstones is the familiar Santa Cruz mudstone that makes up the rest of the cliff (see full outcrop in image 4).




Formation of the Panther Beach Outcrop: The World’s Largest Sedimentary Injection Deposit
When geologists see large sections of rock that are unrelated to the surrounding rock, we often think of some surface process like motion along a fault, that may bring two different rock types in contact. However, at Panther Beach there is no evidence for a fault that could have brought the sandstones to the surface. So how did this ~100m section of sandstone become emplaced in a cliff that is otherwise made of Santa Cruz mudstone?
To understand the formation of the Panther beach outcrop we must start about 1 kilometer below the seafloor. Around 9 million years ago off the coast of ancient Santa Cruz, 1000 meters of mud (the Santa Cruz mudstone) was deposited at the bottom of the ocean above a thick sand deposit (the Santa Margarita sandstone). Later, after heat, and pressure turned most of these sediments into rock, the only sediments left were small pockets of Santa Margarita sands that had not been lithified (i.e., turned to rock). Portions of these sand pockets were rich in oil, which created two distinct reservoirs: oil-rich sands and oil-poor sands. These two sand types were spatially separated because of the density difference between oil and water (see image 5).
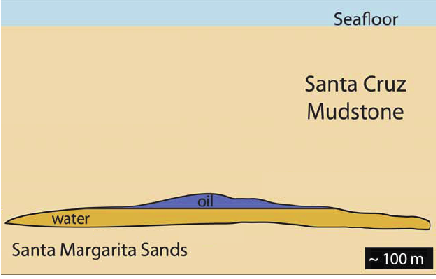
As more mud was deposited atop the Santa Margarita Sands, the pressure on the sand built. Then finally a geologic event, probably either an earthquake or a landslide, shook the sediments causing the slurry of both oil-rich and oil-poor sands to be injected, at a high velocity, into the overlying rock through fractures in the Santa Cruz mudstone. This type of formation is called a sediment injection deposit, where sediments from below are squeezed up into the overlying strata like a tube of toothpaste (see image 6). While the sands were injected, the oil-rich sand slurry would have traveled slower than the oil-poor sands, leaving the oil rich sands below the oil-poor sands. Injection deposits occur in other places on Earth, but the Panther Beach outcrop is the largest sedimentary injection deposit in the world!
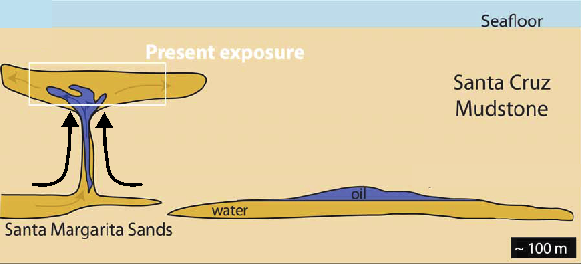
Getting to the Panther Beach Outcrop

Panther Beach is located off Highway 1 about 5 miles north of Santa Cruz. The parking lot for beach access is unmarked but can be found on google maps. The walk to the beach is about 50 yards down a narrow, steep trail (see the image at the start of this post for the view from the top of the trail). Once on the beach, turn left and walk under the arch in the cliff (see image 7). Be careful, this passageway may not be accessible at high tide, use caution when walking through and do not try to pass when water is high! The sedimentary injection deposit makes up the sea cliff beyond the south side of the arch.
The GPS coordinates for Panther Beach are: 36.994, -122.169
Much of the information for this edition of Rock Record was first published in the journal article: Emplacement and dewatering of the world’s largest exposed sand injectite complex, by Timothy Sherry and others.
Reference cited:
Sherry, T. J., Rowe, C. D., Kirkpatrick, J. D. & Brodsky, E. E. Emplacement and dewatering of the world’s largest exposed sand injectite complex. Geochemistry, Geophys. Geosystems 13, 1–17 (2012).

